Page 9 - Part-A
P. 9
Information, Advice or Guidance
Common examples include:
• Doctors’ surgery
• Council office
• Post office
• Careers advisor.
You may have thought of other examples.
The key differences between information, advice and guidance.
Information in the workplace is often obtained by:
• Clients either coming into the workplace in person or by telephoning to ask
questions (for example, ‘What are your opening times?’,
or, ‘Could you give me the phone number for…’).
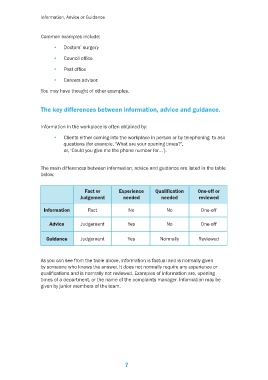
The main differences between information, advice and guidance are listed in the table
below.
Fact or Experience Qualification One-off or
Judgement needed needed reviewed
Information Fact No No One-off
Advice Judgement Yes No One-off
Guidance Judgement Yes Normally Reviewed
As you can see from the table above, information is factual and is normally given
by someone who knows the answer. It does not normally require any experience or
qualifications and is normally not reviewed. Examples of information are, opening
times of a department, or the name of the complaints manager. Information may be
given by junior members of the team.
7